Flange distance is a camera spec you should understand
A Nikon lens engineer explains.
We may earn revenue from the products available on this page and participate in affiliate programs. Learn more ›
Last week Nikon announced it’s highly anticipated line of full-frame mirrorless Z cameras and a brand new FTZ mount that would allow Nikon DSLR shooters to use their older F mount lenses with the new camera. Some photographers were hopeful that the new line of mirrorless cameras would use the same F lens mount and eliminate the need for a mount, unfortunately designing a mirrorless camera system like this would be very difficult because of a little thing called flange distance.
In a new video from the camera brand, optical engineer Atsushi Suzuki, gives an in-depth explanation about what flange distance is and how it affects image quality.
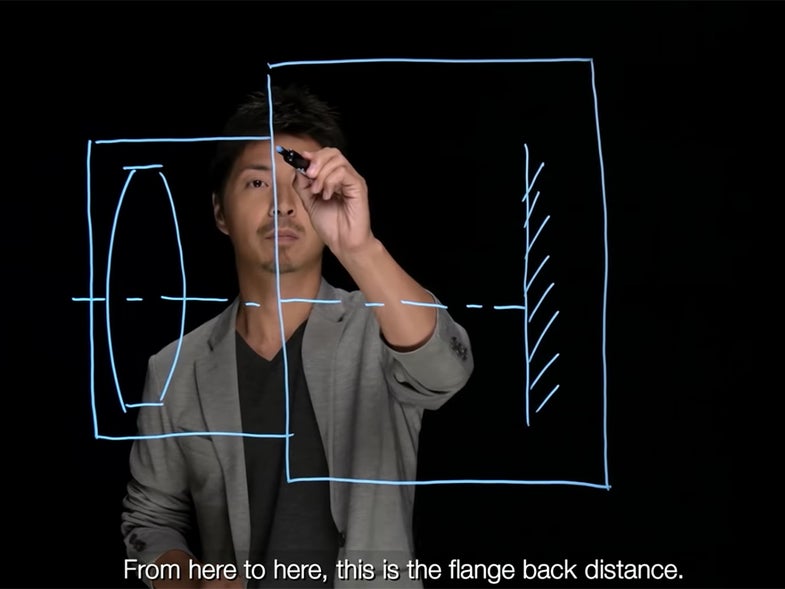
The flange distance refers to the space between where the lens is mounted to the camera body and to the camera’s image sensor. The shorter a flange distance, the smaller and lighter a camera body can be. On Nikon F mount lenses the flange distance is 46.5mm. Nikon’s new Z cameras have a 16mm flange distance and a 55mm inner mount diameter—these measurements are what make it possible for the camera to work with fast lens like the f/1.2 and even a f/0.95. It’s also what allows the body of the new camera to be so small and light, at least compared to the bigger DSLRs.

The combination of this short flange distance and the large inner mount diameter allow large diameter lenses to get closer to the image sensor—the design also allows the lenses to focus more quickly thanks to the placement of the powerful actuator.
Essentially the new lens mount has allowed Nikon lens engineers to begin creating more advanced lenses than we’ve seen in the past.
Check out the full video explainer above for more details.
